
Respiratory occupational hazards and protection of coal dust (coal silica dust)
2024-07-26 16:33Respiratory occupational hazards and protection of coal dust (coal silica dust)
(1) The definition of coal dust (coal silica dust)
Coal dust is coal particles produced by coal seam mining, with a particle size of less than 0.75-1 mm and free silica < 10%.
There are not many workers who are really in contact with pure coal dust, and most of them are in contact with coal and silicon mixed dust.
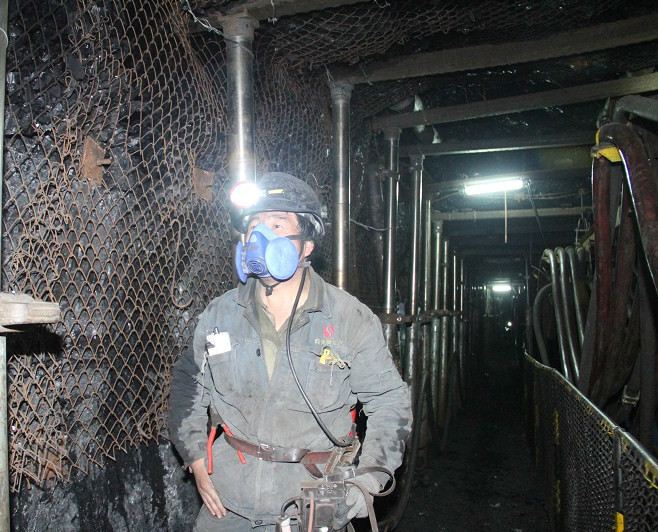

(2) Examples of industries producing coal dust
Examples of industries that produce coal dust (coal-silica dust) are as follows:
1. Coal mining and selection industry: coal drilling, coal blasting, coal reinforcement, coal drilling, blasting coal, hydraulic coal mining, mechanical coal mining, coal loading, coal transportation, coal support, underground ventilation, coal auxiliary, coal preparation and transportation, coal screening, coal crushing.
2. Electricity, steam, hot water production and supply industry: coal, coal grinding, furnace, boiler ash, boiler maintenance
3. Coking, gas and coal products: raw coal transportation, coking coal preparation, coking coal washing, coking coal preparation, coking coal blending, coking distillation, quenching, coking transport, coking auxiliary, coal crushing, coal products production.
4. Alkali products manufacturing: lime forging, potassium alkali forging carbonization.
5. Inorganic salt manufacturing: sodium sulfide production, barium carbonate production.
6. Cement manufacturing: cement feeding, homogenization, pulverized coal preparation, transportation.
7. Graphite and carbon products: carbon grinding, calcination, screening, batching, synthesis.
8. Ironmaking: pulverized coal operation
9. Heavy non-ferrous metal smelting: zinc ore roasting
10. Electrical Machinery and Equipment Manufacturing: Battery sealing.

(3) Respiratory occupational hazards of coal dust
Coal workers' pneumoconiosis is a general term for lung diseases caused by coal miners' long-term inhalation of dust in the production environment.
Coal lung is the pulmonary fibrosis caused by long-term inhalation of coal dust (free silica < 10%).
Long-term inhalation of a large amount of coal silica dust caused by pulmonary fibrosis disease called coal silicosis.
1. Causes of disease
The incidence of coal workers' pneumoconiosis is related to the following factors:
(1) There are few simple coal dust in the productive environment, usually a variety of dust exists, and it should be considered that the mixed dust will have a joint effect.
(2)The individual factors and health status of workers also play a certain role in the occurrence of coal workers' pneumoconiosis, especially rheumatoid pneumoconiosis, which is a manifestation of pneumoconiosis unique to coal miners.
(3) The higher the content of free silica in coal dust, the shorter the onset time and the more serious the lesions
(4)The occurrence and pathological degree of coal workers' pneumoconiosis are related to the accumulation of dust in the lung, which mainly depends on the concentration, dispersion, exposure time and protective measures of dust. The higher the dust concentration, the greater the dispersion, the longer the dust exposure, the worse the protective measures, the greater the amount of dust inhaled and accumulated in the lung, the more prone to pneumoconiosis, the more serious the condition, Symptoms and hazards
2. Symptoms and hazards
Coal workers' pneumoconiosis is a progressive disease, and once it occurs, it can continue to develop even if it is removed from coal dust operations.
Early coal workers pneumoconiosis patients mostly have no clinical symptoms, with the increase of age and the progression of pneumoconiosis disease, respiratory symptoms gradually appear, such as cough, sputum, chest tightness, shortness of breath and so on. Late coal workers pneumoconiosis patients cough, sputum more symptoms, the degree of symptoms is also more serious, cough up mostly black mucous sputum, can appear sitting breathing, can not lie down. In the middle and late stage, pulmonary tuberculosis, spontaneous pneumothorax and pulmonary heart disease can be complicated, and patients with low lung function and immune function can easily induce lung and bronchial infection in autumn and winter, which can aggravate the disease and even death. In severe cases, due to extensive pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema, the lung ventilation area is significantly reduced, pulmonary circulation disorders, pulmonary heart disease can occur, and finally lead to heart and lung failure.

(4) Respiratory protection of coal dust
According to the national product quality standard GB 2626-2019 <Respiratory protection - Non-powered air-purifying particle respirator> and the national document <Standard for Management of Labor Protection Articles of Employers>, coal dust is non-oily particulate matter, and KN90, KN95 and KN100 filter elements can be selected.
After wearing a dust mask, the concentration of particles penetrating the mask (that is, inhaling the human body) is < the occupational exposure limit, and the protection level of the selected dust mask is safe. Otherwise, it is an unsafe dust mask.

For example, the concentration of coal dust (free SiO2 content < 10%) in the environment is 100 mg/m3, and according to the national standard GBZ 2.1-2019
<Occupational exposure limits for hazardous agents in the workplace ̶ Part 1 : Chemical hazardous agents> the occupational exposure limit PC-TWA(Expiratory dust) is 2.5 mg/m3.
Table 1 Comparison of coal dust prevention effect of Non-powered air-purifying particle respirator with filter grade 95 and 100
Respirator filtration level | KN95 | KN100 |
Filter efficiency | 95% | 99.97% |
Penetration rate | 5% | 0.03% |
Concentration of coal dust (exhaled dust) in the air of workplace(mg/m3) | 100 | |
Penetration concentration of coal dust (exhaled dust) (mg/m3)
| 5 | 0.03 |
Coal dust (exhaled dust) occupational exposure limits PC-TWA(mg/m3) (Free SiO2 content < 10%) | 2.5 | |
Inhaled coal dust exceeding occupational exposure limits | 1 times | <Occupational exposure limit |
Result | Exceeding the national standard limit 1 times | Not exceeding the national standard limit |
According to the table, although the filtration efficiency of KN100 and KN95 grades is only 4.97% different, the penetration rate of KN95 grades is 167 times that of KN100 grades.
Due to the cumulative nature of coal worker's pneumoconiosis/coal silicosis, it is recommended to use KN100 grade dust masks to protect against coal dust.

